Human resource management (HRM) is the process of managing an organization’s manpower in a way that maximizes productivity and effectiveness while also advancing the goals and objectives of the organization. It is a critical function within any organization, as the performance and engagement of employees can have a significant impact on the success of the business.
Table of Contents Covered
Introduction to Human Resource Management
Human resource refers to the individuals who make up the workforce of an organization. These individuals are valuable assets to the organization and need to be managed in a way that supports their growth and development while also aligning with the organization’s goals and objectives. In its purest sense, the term “human resource” refers to the workforce of an organization. In respect of an organization, these people are frequently referred to as workers, staff, or employees. Human resources are essential to any organization because human resource capital is responsible for productivity, innovation, and growth.
Management, on the other hand, is the process of planning, organizing, directing, and controlling an organization’s resources to achieve its goals and objectives. This involves setting objectives and developing strategies, coordinating the efforts of stakeholders, delegating tasks, monitoring performance, and creating a positive work environment.
Combining these two concepts, Human Resource Management is the process of managing an organization’s workforce in a way that aims to achieve the organization’s goals and objectives. This involves recruiting and hiring the right people at the right place, providing them with the necessary training and development, managing their performance, and creating a positive work environment that fosters employee engagement and satisfaction. Effective human resource management is essential for achieving organizational success, as it helps ensure the organization has the talent and resources it needs to achieve its strategic goals and objectives.
At its core, Human Resource Management is about managing the employment relationship between an organization and its employees. This includes activities such as recruitment, selection, training and development, performance management, compensation and benefits, and employee relations. Effective HRM practices can enhance employee motivation and commitment, leading to improved productivity, customer satisfaction, and overall organizational performance.
This article provides a comprehensive overview of the complete process of human resource management practices in most organizations. It explores and provides practical guidance on how to design, implement, and evaluate HRM programs and initiatives. Whether you are a seasoned HR professional or new to the field, it will help you to navigate the complex and dynamic world of Human Resource Management and contribute to the success of your organization.
The main human resource management process involves 4 major steps. The following are the steps in human resource management.
- Acquisition
- Training and Development
- Motivation and Utilization
- Maintenance and Retention
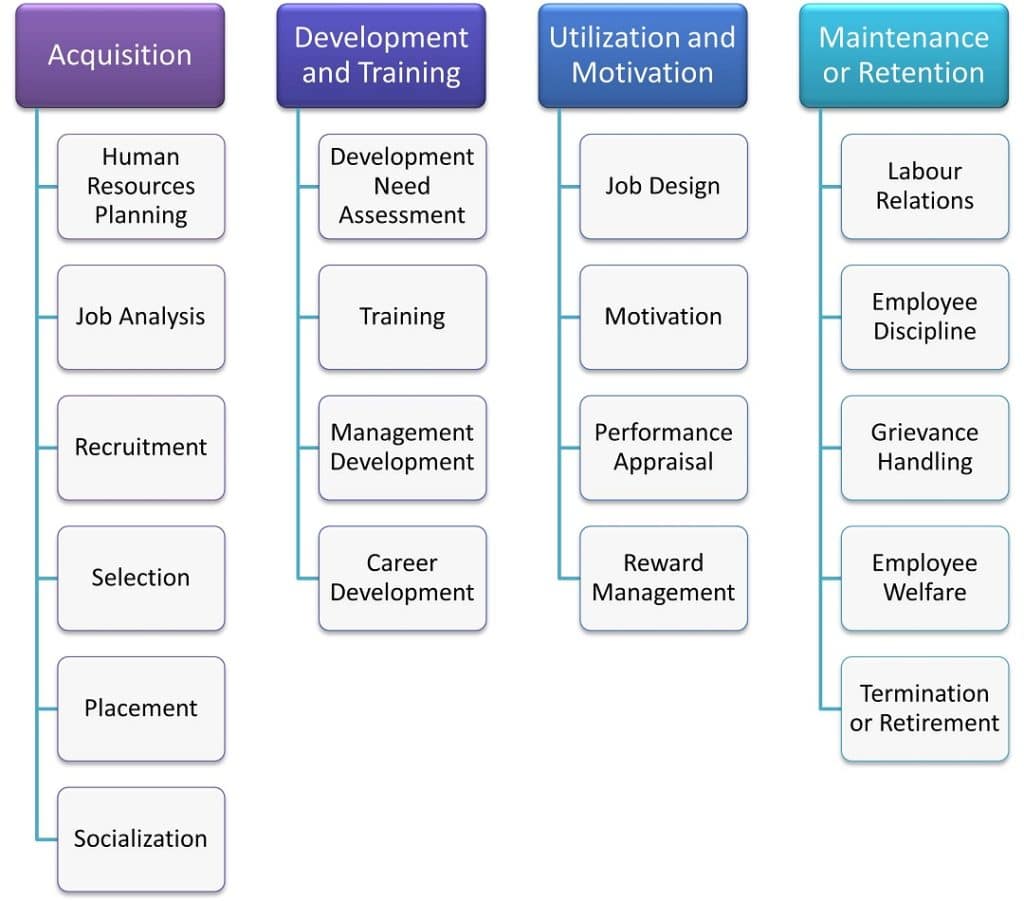
1. Acquisition
The acquisition is the first step or function of Huaman Resource Management. It is majorly concerned with analyzing the demand and supply of human resources and full the required position through internal restructuring and recruitment of new personnel. To accomplish this, the Human Resource Manager should make a human resource management action plan, and analyze the job in terms of description and specification.
According to human resource plans, the organization will either promotes and transfer personnel internally or hires externally through open vacancy specifying job requirement and describing the job. This process is completed by the human resource department through a series of selection procedures including shortlisting, selection tests, physical interviews, etc.
The acquisition process also includes the placement phase and socialization phase which ensures the actual placement of the hired employee in the right place as planned and advertised while accepting applications. The socialization process is concerned with introducing new employees to the organization, workplace, and with seniors and sub-ordinates.
a. Human Resource Planning
Planning is the process of setting goals, objectives, and strategies to achieve a desired outcome. It involves analyzing the current situation, identifying future opportunities and challenges, and making decisions about what actions to take to achieve the desired results. Human Resource Planning is the same as planning but in terms of human resources management.
It sets goals, objectives, and strategies for managing human resources to achieve the desired outcomes. It involves analyzing or accessing the current human resource, forecasting the demand for human resources, and forecasting the future supply of human resources. This process then matches the demand with the supply and finds out whether the organization has a situation that requires changes in the current human resource and makes a well-defined action plan.
In-depth, the human resource planning process involves the following steps.
i. Assessing Current Human Resources
Assessing current human resources involves evaluating the current workforce in terms of their skills, abilities, experience, and potential. This step helps organizations to understand their current workforce’s strengths and weaknesses, including identifying any gaps in the workforce’s knowledge and skills. Through this assessment, organizations can identify opportunities for employee development and make decisions about recruitment, training, and promotion.
Assessing the current human resources means looking at the people who work for a company and figuring out their skills, experience, and potential. This helps the company understand what the employees are good at and what they need to work on. By doing this, the company can decide how to train and promote their employees, and even how to hire new people. A company needs to know all about its workers so it can make sure everyone is doing their best and the company can be successful.
ii. Forecasting Demand
In human resource management, forecasting demand is the process of predicting the number of employees that an organization will need in the future. This step involves analyzing the organization’s business goals, objectives, and strategies and considering the external factors that might impact the organization’s staffing needs, such as industry trends and economic conditions. The forecasted demand is used to determine the number and types of employees required to meet the organization’s goals and objectives.
iii. Forecasting Supply
Forecasting supply is the process of predicting the number of employees that will be available in the labor market to meet the organization’s needs. This step involves analyzing the internal and external factors that might impact the availability of the workforce, such as employee retirements, resignations, and promotions. The forecasted supply is used to determine the potential candidates available for the organization’s future workforce.
iv. Matching Demand with Supply
Matching demand with supply is the process of comparing the forecasted demand and supply to identify any discrepancies between the two. This step involves analyzing the current workforce’s skills and the future workforce’s required skills to determine any skill gaps that need to be filled. By matching demand with supply, organizations can identify potential recruitment and training needs to ensure that they have the right number and types of employees required to meet their objectives.
v. Action Plan
The action plan involves developing a plan of action to address any discrepancies between the forecasted demand and supply. The plan includes specific steps to be taken to ensure that the organization has the right number and types of employees required to meet its objectives. The action plans involve primarily two components. One is managing the human resources available in the organization most efficiently and then systematically hiring from external sources for the remaining vacant position.
Promoting or Downsizing Existing Personnel
Promotion is a common practice in the human resource management process. Promoting or downsizing existing personnel involves considering the current employees’ skills and experience to determine if they are suitable for new roles in the organization. If employees are not suitable for new roles, organizations may need to consider downsizing. On the other hand, if employees are suitable for new roles, organizations can promote employees to fill any skill gaps that can be filled with internally available resources.
Recruiting New Personnel From External Sources
Recruiting new personnel from external sources involves evaluating, assessing, and selecting potential candidates available in the labor market. This step involves creating job descriptions, posting job ads, conducting interviews, and selecting the most suitable candidates. Recruitment is often required when the organization’s demand exceeds the supply of its current workforce. By recruiting new personnel, organizations can fill any skill gaps and ensure that they have the right number and types of employees to meet their objectives.
b. Job Analysis
Job analysis is a critical component of human resource management. It is a systematic process that HR professionals use to gather information about jobs within an organization. The data collected during job analysis is used to develop job descriptions and job specifications, which provide a detailed understanding of the duties, responsibilities, and requirements for a particular job.
Job analysis can be conducted through several methods, including observation, interviews, questionnaires, and task analysis. Observational methods involve observing employees as they perform their job duties to gain insight into the tasks they perform, the equipment used, and the physical demands of the job. Interviews can be conducted with employees, supervisors, and subject matter experts to gather information about the job’s requirements, responsibilities, and competencies.
Questionnaires can be used to collect data from a large sample of employees, providing more comprehensive data for analysis. Task analysis involves breaking down a job into its parts and analyzing each task’s requirements.
Job analysis is essential for several HR functions, including recruitment, selection, training, performance appraisal, and compensation. For example, job analysis helps HR professionals identify the knowledge, skills, and abilities required for a job, which can be used to develop selection criteria and job-specific training programs.
Similarly, job analysis can help HR professionals design performance appraisal systems that accurately assess an employee’s performance based on the requirements of the job.
In human resource management, job analysis helps to outline and formulate two major components of jobs. They are Job Description and Job Specification.
i. Job Description
Job Description is a very essential component of human resource management. A good job description is a document that outlines the duties, responsibilities, and requirements of a particular job. It is typically used by employers to advertise job openings and to inform potential candidates about the expectations and requirements of the job.
A well-written job description should accurately reflect the tasks and responsibilities of the job, including:
- Job Title: The official title of the job being advertised.
- Objective/Summary: A summary of the purpose and goals of the position.
- Duties and Responsibilities: A detailed list of the daily tasks and responsibilities required for the position.
- Qualifications: The minimum requirements for education, skills, and experience necessary to perform the job effectively.
- Physical Requirements: Any physical demands that are necessary to perform the job, such as lifting or standing for long periods.
- Physical Demands: This section describes any physical requirements of the job, such as lifting heavy objects, standing for long periods, or working in extreme temperatures.
- Work Environment: The work environment, including any relevant conditions or hazards associated with the job.
- Salary and Benefits: Information about the compensation and benefits package that will be offered to the successful candidate.
- Equipment and Tools Used: This section lists the tools, equipment, and materials required for the job, such as computers, vehicles, machinery, or specialized equipment.
- Other Duties: Finally, the job description may include a catch-all section for any other duties or responsibilities that may be required of the employee, even if they are not specifically listed elsewhere in the job description.
Overall, a job description should be clear, concise, and informative. It should accurately reflect the job’s nature and the employer’s expectations for the successful candidate. A well-written job description can help attract qualified candidates and ensure that the hiring process is efficient and effective.
ii. Job Specification
Job specification refers to the detailed qualifications, skills, experience, and attributes that a person must have to perform a specific job. It outlines the specific requirements that are necessary for the job holder to perform their duties effectively. A job specification includes details such as educational qualifications, work experience, skills, physical and mental requirements, personal traits, and abilities that are essential for successful job performance.
Job specifications are prepared through a systematic job analysis process that involves identifying the specific job duties and responsibilities, as well as the skills and qualifications required to perform them. Once the job analysis is complete, the job specification is developed by matching the required skills and qualifications with the job duties and responsibilities. A job specification is an important tool for recruitment and selection, as it ensures that only candidates with the required skills and qualifications are considered for the job.
Here are some of the points that may be included in a job specification:
- Education and qualifications: This includes the level of education and any required certifications or licenses.
- Experience: The number of years of experience required, the type of experience, and any specific skills or knowledge needed.
- Skills and abilities: The specific skills and abilities necessary to perform the job, such as computer skills, communication skills, and physical abilities.
- Knowledge: Any specialized knowledge that is required for the job, such as knowledge of specific software programs, industry regulations, or technical skills.
- Personal characteristics: Certain personal characteristics may be important for the job, such as being detail-oriented, organized, or able to work well under pressure.
- Working conditions: Information about the working conditions, such as the physical demands of the job, the work schedule, and any travel requirements.
iii. Difference Between Job Description and Job Specification
While studying human resource management people often get confused between Job Descriptions and Job specifications. They are different from each other. Here is the difference between Job Descriptions and Job Specifications.
| Job Description | Job Specification |
|---|---|
| A written statement that provides an overview of the job duties and responsibilities. | A document that outlines the knowledge, skills, and abilities required to perform a job effectively. |
| Describes the tasks and responsibilities associated with a particular job. | Identifies the qualifications and competencies required to perform the job. |
| Typically written in a narrative format. | She is usually presented in a bullet-point format. |
| Provides information about the job’s reporting structure, work schedule, and physical requirements. | Outlines the education, experience, and training needed to perform the job effectively. |
| This may include future expectations and potential growth opportunities for the position. | Used for selecting and evaluating candidates for the job. |
| Typically focuses on the current job requirements. | This may include future expectations and potential growth opportunities for the position. |
| Usually prepared by the HR department in consultation with the relevant department or supervisor. | Can be prepared by the HR department or the relevant department or supervisor. |
| Helps employees understand the expectations and requirements of their job. | Helps HR professionals develop job-specific training programs and performance appraisal systems. |
| A useful tool for managing employee expectations and setting performance standards. | Helps HR professionals develop fair and objective selection criteria. |
| Provides a clear understanding of the job’s role within the organization. | Helps HR professionals design compensation and benefits packages that are appropriate for the job. |
c. Recruitment
Recruitment is one of the primary functions performed by human resource management in the acquisition process. This acts as a step to fulfill a vacant position with the right men in the right place. It first recruits from within the organization as per the action plan.
Most of the time, internal recruitment fulfills some positions and at the same time also makes other posts vacant in case of a promotion or demotion plan. In rare cases, an organization may restructure the human resources so as to perfectly utilize the available resources without requiring external recruitment.
i. Internal Recruitment
Internal recruitment is the process of filling a job position within an organization by considering existing employees for the role. This method is beneficial for the organization as it can motivate existing employees to work harder and achieve career growth. The internal recruitment process can be initiated through job postings, employee referrals, or promotions. Internal recruitment can also lead to increased employee loyalty and retention, as employees feel valued and recognized within the organization.
ii. External Recruitment
External recruitment is the process of attracting candidates from outside the organization to fill job vacancies. It involves advertising job vacancies through various channels such as online job portals, recruitment agencies, job fairs, and social media platforms. External recruitment can be beneficial for the organization as it can bring in fresh perspectives and diverse skill sets that may not be available within the organization. However, it can be a time-consuming and expensive process as it involves sourcing, screening, and interviewing potential candidates.
Sometimes external recruitment can be done through direct connections and contacts without opening vacancies. This is suitable when the organization can identify a suitable person for the post in terms of ability, confidentiality, and cost-effectiveness. Poaching is one example where an organization makes an unethical practice of theft of competitors’ employees.
Selection
The selection process is one of the most essential functions of human resource management as it plays a crucial role in determining the suitable candidate to be chosen from among the pool of applicants. It involves various stages and assessments that help in evaluating the qualifications, skills, and fit of each individual in relation to the job requirements and organizational goals. Additionally, the selection process entails careful consideration of factors such as experience, educational background, personality traits, and potential for growth and development.
By meticulously analyzing these aspects, the human resource department can make an informed decision that aligns with the company’s vision and objectives, ultimately contributing to the overall success and productivity of the organization. So, the selection process holds immense significance as it ensures that only the most competent and promising candidates are selected for employment opportunities.
The selection process consists of the following procedures to be specific.
Application Evaluation
The evaluation of applications is a crucial step in the selection process of human resource management. It involves carefully reviewing and assessing the submitted applications to determine the qualifications, skills, and experiences of the candidates. The evaluation process aims to identify candidates who possess the necessary competencies and expertise required for the job position.
Human resource professionals carefully analyze the information provided in the applications, including educational background, work experience, certifications, and any additional relevant details. By evaluating applications thoroughly, organizations can shortlist candidates who meet the initial criteria and proceed to the next stage of the selection process.
Preliminary Interview (Short Listing)
Shortlisting plays a crucial role in the selection process of human resource management, coming after the initial evaluation of applications. Its purpose is to narrow down the pool of candidates based on specified criteria and identify those who are the best fit for the job. Human resource professionals are responsible for this process, where they compare the qualifications, skills, and experiences of the applicants with the job requirements outlined in the job description.
The goal is to create a shortlist of candidates who show the greatest potential for success in the role. This involves carefully considering factors like relevant work experience, educational background, specialized skills, and other job-specific requirements. Once the shortlisting is done, the chosen candidates are typically invited for further assessments or interviews to evaluate their suitability for the position in greater depth.
Selection Tests
The selection test is an integral part of the selection process of human resource management and is designed to assess various aspects of a candidate’s abilities and suitability for a particular job. It typically consists of different types of tests, including aptitude tests, intelligence tests, personality tests, and achievement tests.
Aptitude Tests
Aptitude tests are used to evaluate a candidate’s natural or acquired skills and abilities in specific areas. These tests can cover a wide range of areas such as numerical reasoning, verbal reasoning, logical reasoning, and problem-solving. By assessing aptitude, employers can determine if candidates possess the necessary abilities to perform well in certain job roles.
Intelligence Test
Intelligence tests measure a candidate’s cognitive abilities, including reasoning, analytical thinking, and problem-solving skills. These tests help employers understand a candidate’s overall intellectual capability and potential for learning and adapting to new situations.
Personality Test
Personality tests aim to assess an individual’s personality traits, behavioral patterns, and work preferences. These tests provide insights into a candidate’s interpersonal skills, teamwork abilities, leadership potential, and compatibility with the company’s culture and values. By evaluating personality, employers can identify candidates who are likely to thrive in specific work environments and contribute positively to the team.
Achievement Test
Achievement tests focus on assessing a candidate’s knowledge and skills in a particular domain relevant to the job position. To be specific, it tests the experience of the candidate in the same or similar field. These tests are often used to evaluate technical expertise, subject matter knowledge, and specific job-related competencies. They help employers gauge an applicant’s level of proficiency and expertise in areas critical to the role.
During the selection process, these tests are administered to candidates, either online or in person, depending on the organization’s preferences. The results of these tests provide valuable information to employers, allowing them to make informed decisions about the most suitable candidates for the job.
It’s important to note that selection tests are just one component of the overall assessment process, and they are typically combined with other evaluation methods such as interviews, references, and background checks to make comprehensive hiring decisions.
Reference Check
Reference checks play a crucial role in the selection process as they provide employers with invaluable insights into a candidate’s background, work history, and character. By reaching out to individuals who have closely collaborated with the candidate in previous roles, employers can gather feedback and verify the information provided. The primary objective is to validate the candidate’s qualifications, skills, and experiences, enabling employers to gain a comprehensive understanding of their performance, work ethic, and suitability for the position at hand.
During the reference check, employers proactively engage with references, posing relevant questions concerning the candidate’s job performance, strengths, weaknesses, teamwork abilities, and professionalism. This comprehensive approach facilitates an in-depth evaluation of the candidate’s fit within the organization’s culture, as well as their integrity and ethical conduct. While conducting reference checks, employers must exhibit a strong adherence to professionalism, utmost respect for confidentiality, and strict compliance with data protection laws. It is essential to consider reference checks in conjunction with other assessment methods to ensure a well-informed decision-making process.
Final Interview
The final interview is a crucial stage in the human resource management process where the top candidates are assessed in more detail to determine the best fit for the position. Its purpose is to delve deeper into the candidate’s qualifications, skills, experiences, and overall suitability for the role.
Interview Content
During the final interview, the candidates may be asked a range of questions that explore their expertise, problem-solving abilities, decision-making skills, and their alignment with the company’s values and culture. Practical exercises or simulations may also be conducted to assess the candidate’s skills and capabilities in real time. Interviews also check if the candidate is able to handle stressful situation and checks the ability of the decision-making capacities in a critical situation.
The final interview is an important opportunity to evaluate the candidate’s compatibility from a personal and cultural standpoint. The interviewers may delve into the company’s values, mission, and expectations to ensure that the candidate shares the same organizational culture and can work well within the team dynamic. Similarly, the candidate may have the chance to inquire about the company’s objectives, work environment, and future opportunities, gaining a deeper understanding of the organization.
After the last interviews are done, the hiring team looks at the feedback and assessments from each candidate. They think about different things, like how the candidate did in the interview, their qualifications, and how well they fit with the team and the organization. This evaluation helps them choose the final candidate who will be offered a job.
Medical Test
Medical tests are essential for certain positions, particularly those that require physical fitness or have specific health-related requirements. These tests are conducted to evaluate the candidate’s medical fitness and ensure that they are capable of performing the duties associated with the job without endangering themselves or others.
The specific medical tests required may vary depending on the nature of the position and the industry. Some common types of medical tests include:
- Physical Examinations: The candidate’s overall health and fitness are carefully assessed through a comprehensive physical examination. This examination incorporates measurements of height, weight, blood pressure, vision, and hearing tests, alongside an evaluation of the candidate’s general medical history.
- Drug and Alcohol Tests: In safety-sensitive roles or industries where substance abuse can pose a risk, candidates may be required to undergo drug and alcohol testing. These tests can detect the presence of illegal drugs or alcohol in the candidate’s system.
- Fitness Assessments: For physically challenging jobs, like those in the military or emergency services, applicants might go through fitness assessments. These assessments check the person’s strength, stamina, flexibility, and cardiovascular fitness to ensure they can handle the physical requirements of the position.
- Health Questionnaires: Prospective job candidates may be required to fill out comprehensive health questionnaires. These questionnaires aim to gather essential information regarding the applicant’s medical history, current medications, and any pre-existing health conditions that could potentially influence their capability to perform the job safely.
- Specific Medical Tests: Depending on the job requirements, additional specialized medical tests may be conducted. For example, jobs that involve working with hazardous materials may require lung function tests or respiratory assessments. Jobs involving driving or operating heavy machinery may require vision and hearing tests.
The results of the medical tests are typically assessed by qualified medical professionals, who determine whether the candidate meets the health and fitness requirements necessary for the job. The information gathered during these tests is treated with confidentiality and in compliance with relevant privacy and medical regulations.
Placement
Placement is the process of assigning selected candidates to roles or departments within an organization. It involves evaluating their qualifications, experience, and preferences, and aligning them with the organization’s needs and requirements. This ensures the optimal use of talent, contributing to a productive and successful environment.
Placement typically involves the following:
- Job Assignment: The selected candidate is assigned to a particular job role based on their qualifications, experience, and the needs of the organization. This may involve considering factors such as the candidate’s expertise, career goals, and potential for growth within the role.
- Department or Team Placement: The candidate is placed within a specific department or team that aligns with their skills and the needs of the organization. This ensures that they can collaborate effectively with their colleagues and contribute to the overall goals of the department or team.
- Onboarding Process: Once placed, the candidate goes through an onboarding process, which includes orientation and familiarization with the organization’s policies, procedures, culture, and work environment. This helps the candidate integrate smoothly into their new role and fosters a sense of belonging within the organization.
Socialization
Socialization is a process through which selected candidates become integrated into the organizational culture and form connections with their colleagues. It involves introducing the new employees to the social and professional aspects of the organization, facilitating their adjustment, and helping them become productive members of the team.
The socialization process may include the following elements:
- Introduction to Colleagues: The new employees are introduced to their colleagues and team members. This may involve informal meetings, introductions, or team-building activities to foster positive relationships and create a sense of camaraderie.
- Mentoring and Support: Assigning a mentor or buddy to the new employees can help them navigate their initial days in the organization. Mentors provide guidance, answer questions, and offer support to ensure a smooth transition and help the new employees feel welcome.
- Training and Development: Providing training and development opportunities to new employees helps them acquire the necessary skills and knowledge for their roles. This enhances their confidence and enables them to contribute effectively to the organization.
- Integration into Organizational Culture: The socialization process also involves familiarizing the new employees with the organization’s values, norms, and practices. This includes communicating the organization’s mission, vision, and goals, as well as the expected behaviors and standards of conduct.
- Ongoing Support: Continued support and communication with the new employees are crucial to their socialization process. Regular check-ins, feedback sessions, and opportunities for open dialogue help address any concerns, provide guidance, and ensure their ongoing integration into the organization.
Effective socialization of selected candidates promotes a positive work environment, enhances employee engagement, and contributes to their long-term success within the organization. It helps them develop a sense of belonging, establish professional relationships, and become aligned with the organization’s goals and values.
2. Training and Development
Training and Development is the second step in the human resource management process. In order to make the human resource capable of executing the delegated job, the fundamental thing organization can do is assess training needs and provide appropriate training as necessary. The organization may provide basic training on how to operate at that level which can be completed automatically at the workplace during working hours, it can also be called on-the-job training. For advanced and new work, the organization may provide dedicated off-the-job training through Classroom Lectures and Conferences, Audio Visual Aids, Simulation Exercises, Programmed Instructions, Case Studies, Sensitivity Training, and Computer Aided Instructions, etc.

While development is a wider term than training in many aspects, the organization may have to conduct a detailed development need assessment through organizational level analysis, task level analysis, and personal level analysis. After assessment organization may contribute to management development and the career development of human resources. Career development refers to making personnel ready or capable of functioning at a higher level than the existing level. On the other hand management development includes preparing the personnel for managerial decisions ability and executing managerial responsibilities.
3. Motivation and Utilization
The utilization phase of human resource management is related to the maximum utilization of the available human resource to get an optimum level of output while keeping the employees still motivated and ready to serve in the position. It is an ethical exploitation of the optimal capacity of human resources while keeping them happy and satisfied.
In the classical approach, the monetary factor was considered to be the factor to extract the maximum output from human resources. But in the modern approach, it is understood that while money is a major motivational factor, there are some other major factors that can contribute to the utilization process of human resources in the same way that money does. Some factors that help in human resource utilization are Job design, performance appraisal, motivational factors which can be monetary or financial, and non-financial factors such as recognition reward, authority, active participation, or stake.
In the utilization process, the most pervasive factor is psychological factors such as motivation and a feeling of attachment to the organization and its management, position in the organization, and delegated task authority and responsibility in the organization.
4. Maintenance and Retention
The retention and maintenance phase of human resource management (HRM) is a crucial element of an organization’s human resource strategy, as it aims to maintain the existing workforce by managing various factors. These factors include labor relations, employee discipline, grievance handling, employee welfare, and termination or retirement. Effective management of these factors can lead to a positive work environment, increased productivity, and employee satisfaction.
To achieve effective labor relations, organizations must establish trust and mutual respect between management and employees by being transparent, providing fair compensation and benefits, and establishing clear communication channels. Additionally, employee discipline involves setting clear rules and regulations, and corrective actions in case of any violations, leading to a productive work environment and a decrease in employee misconduct.
Grievance handling is related to addressing employee complaints and concerns. It can improve employee morale, resolve conflicts, and minimize negative impacts on the organization. An efficient and transparent grievance handling process is crucial to promptly and effectively address employee concerns.
Employee welfare is also an essential action to be considered in human resource management for providing a safe and healthy work environment, training and development opportunities, and employee benefits such as health insurance, retirement plans, and paid time off. Investing in employee welfare can improve employee satisfaction and reduce turnover rates.
Finally, termination or retirement is an important aspect of human resource management, requiring clear policies and procedures to ensure compliance with legal and ethical standards. By doing so, the organization can minimize negative impacts on its reputation while ensuring a fair and respectful exit for employees.
In conclusion, the retention and maintenance phase of HRM is essential in creating a positive work environment, increasing productivity, and improving employee satisfaction. By managing labor relations, employee discipline, grievance handling, employee welfare, and termination or retirement, organizations can retain their best employees and succeed in the long run.
Conclusion
In summary, human resource management is the process of managing an organization’s workforce to achieve its goals and objectives. The process includes four major steps: acquisition, training and development, motivation and utilization, and maintenance and retention. Effective human resource management is essential for achieving organizational success, as it helps ensure the organization has the talent and resources it needs to achieve its strategic goals and objectives. Each step of the process is important for the successful management of human resources, and each requires careful planning, implementation, and evaluation.